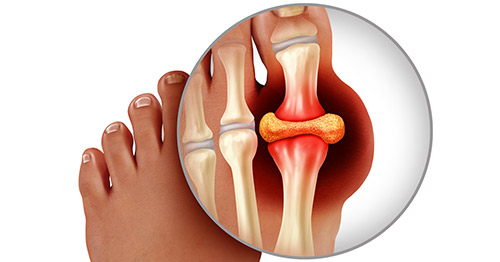
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. When uric acid crystallizes, it tends to deposit in joints, leading to severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness. It usually occurs due to:
- High uric acid levels in the blood (hyperuricemia), often from consuming foods rich in purines (like red meat, seafood, and alcohol).
- Impaired kidney function which prevents the body from effectively eliminating uric acid.
The most common symptoms are swelling, redness, and severe pain in the affected joints, often starting with the big toe but potentially affecting other joints like the ankles, knees, wrists, or elbows.
What are purines?
Purines are naturally occurring compounds found in the cells of your body and in certain foods. They play an important role in your body because they are building blocks for DNA and RNA, as well as essential for energy metabolism.
When purines are broken down during digestion or cell metabolism, they produce uric acid as a byproduct. While most uric acid is excreted through urine, excess uric acid can build up in the bloodstream, potentially leading to gout if uric acid crystals form in the joints.
Sources of Purines
- High-purine Foods:
- Organ meats (liver, kidney)
- Red meats (beef, lamb, pork)
- Seafood (anchovies, sardines, mackerel, mussels, scallops)
- Alcohol (especially beer and spirits)
- Some legumes (lentils, chickpeas)
- Low-purine Foods:
- Fruits and vegetables (except high-purine vegetables like asparagus and spinach)
- Alkaline nuts and seeds
- Herbal teas and water
Note: See Dr. Sebi’s Nutritional Guide
Where is the mucus in the case of gout?
In the case of gout, mucus may accumulate around the affected joints as part of the body’s protective response. Uric acid, being highly acidic, can irritate and damage surrounding tissues, breaking down cell walls. This cellular damage triggers the body to produce excess mucus as a defense mechanism. The mucus serves to neutralize the acidity, protect damaged cells, and help to trap and flush toxins in the affected area. However, with this acidity – and the body producing excess mucus – it creates a problem.
Excess Mucus Becomes Harmful
Excess mucus can circulate with the blood and spread throughout the body, potentially causing harm:
- Blocking Oxygen Supply: Excess mucus can coat cells, depriving them of oxygen, which is essential for cellular respiration and energy production.
- Cellular Dysfunction: Without adequate oxygen, cells switch to anaerobic respiration, leading to a buildup of lactic acid and creating an environment conducive to further acidity and inflammation.
- Disease Development: Oxygen deprivation can weaken cellular function and immunity, potentially creating conditions for chronic inflammation or degenerative diseases to develop.
What to consume: Food that can help include both sweet and tart cherries, berries, tamarind and herbal teas such as shavegrass, dandelion, nettle, ginger, burdock and sarsaparilla, among others.
References:
– Gout In Depth: Risk Factors, Diagnosis and Treatment – https://www.hss.edu/conditions_gout-risk-factors-diagnosis-treatment.asp
– A write up on allopathic & herbal medicine for treatment of gout by Shalini Periyasamy, Sabarinath Chandrasekar, Manimekalai Pichaivelnand Thenmozhi Velmurugan. Published by International Journal of Herbal Medicine 2020; 8(5): 14-22